Rubber Tubes
——————-Here is everything you need to know about rubber tubes on the internet.
What is Rubber Tubes?
Rubber tubing, also known as rubber hose or rubber piping, is made of natural and synthetic rubber and is used to circulate and transport liquids and gases for household and industrial uses. The natural or synthetic rubber materials used for the manufacture of rubber tubing make it extremely flexible, dependable, and resilient for use in hydraulic and pneumatic equipment as well as food processing and medical applications.
Rubber tubing can be produced in a wide variety of tube diameters and wall thicknesses. It is this versatility that has made it adaptable for use in many unique and specialized industrial applications.
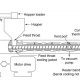
How Rubber Tube is Made?
Rubber tubing is distinctively different from another tubing because of its rubber content, which is an elastomer that has high strength and durability as well as being able to be stretched and deformed without being permanently damaged. This is mainly due to its flexibility, tear-resistance, resilience, and thermal stability.
Rubber tubing is produced using one of two processes. The first method is the use of a mandrel, where rubber strips are wrapped around a pipe and heated. The second process is extrusion, where the rubber is forced through a die.
What are the Materials Used to Make Rubber Tube?
The wide use of rubber tubing has led to the development of several different types of rubber to fit unique and specialized applications. Though there are many varieties of rubber, all types can be divided into natural or synthetic.
Each type of rubber has strengths and weaknesses that are determined by the characteristics of the chosen polymer. Material selection is based on the temperature of the application, chemicals involved, abrasive factors, compression, and load, to name a few.
Different Types of Rubber Tubing
Fluoroelastomer Rubber Tubing (FKM)
Fluoroelastomer rubber tubing is used for high-temperature environments and is resistant to chemicals, oil, and heat above 200°C. The types of FKM are divided according to their fluorine content, which can range between 66% to 70%. FKM tubing with a high fluorine content has increased resistance to fluids.
Butyl Rubber Tubing
Butyl rubber tubing is used for air and carbon dioxide transfer. It has thick walls, is shock absorbent, and is resistant to oxygen degradation with a temperature use range of -30° F to +275° F. Butyl rubber is a combination of isobutylene and isoprene.
Hypalon Rubber Tubing (Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene of CSM)
CSM is made by the chemical treatment of polyethylene with gaseous chlorine and sulphur dioxide. The treatment causes the polyethylene to become flexible, vulcanized rubber. The chlorine creates a flame-resistant and oil-resistant rubber.
Hypalon is a chlor-sulfonated polyethylene that is resistant to oxygen, ozone, and harsh weather conditions. One of its main uses is in applications where there are corrosive chemicals or acids as well as oil and grease. It can be used at temperatures ranging between -30° F to +200° F and retains its tensile strength for long periods of time.
Natural Rubber Tubing (NR)
Natural rubber is made from the fluids of plants and trees and has exceptional mechanical properties such as impact resistance, tensile strength, resistance to abrasion, and tear resistance. It is used for applications that require the highest degree of physical properties but is not used where resistance to chemicals, fuels, oils, or solvents may be involved.
Neoprene Rubber Tubing (Polyisoprene)
Neoprene rubber is a synthetic rubber made from coal, salt, and limestone. It is used in applications that require a resistance to petroleum products, sunlight, ozone, and heat. Neoprene rubber products are mainly used for outdoor applications due to its ability to withstand wide temperature variations. A drawback to neoprene rubber is its electrical conductivity, which limits it from being used in electrically charged environments.
Nitrile Rubber Tubing
Nitrile is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene. It has exceptional properties, which include its resistance to water, petroleum products, and fuels. Nitrile rubber tubing can be exposed to petroleum products for long periods of time without becoming brittle and retains its excellent flexibility.
Styrene-Butadiene Tubing (SBR)
SBR has the same properties as natural rubber though it is a combination of styrene and butadiene. It is resistant to solvents and petroleum products much like latex rubber but has better water resistance than natural rubber. The characteristic of SBR that makes it ideal for manufacturing is its abrasion resistance and low cost.
Silicone Rubber Tubing
Silicone rubber is made from a polymer that is reinforced with silica. It can be used in a wide expanse of environments from extreme cold to very high temperatures and is flame resistant. Silicone tubing is smooth, pliable, elastic, resistant to water, and flexible.
Thermoplastic Rubber Tubing (TPE)
TPE is used in applications that require resistance to harsh and dangerous substances as well as a wide variety of acids. It can handle constant bending and movement, which has made it popular for use in robotics and pumps. TPE can be severely stretched and deformed but return to its original shape without signs of wear. This quality gives it a long life of usefulness.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber Tubing (EPDM)
EPDM is a comonomer that consists of propylene, ethylene, and diene which allows it to be vulcanized with sulfur. It is highly resistant to heat, light, and ozone. When it is properly produced and mixed, it can be used as outside tubing for many years. The main feature that makes it ideal for outdoor use is its ability to withstand temperatures below -40° C. Black carbon, calcium carbonate, and plasticizers are added during the manufacturing process to help give EPDM its rubber properties.
Hytrel Rubber Tubing
Hytrel rubber tubing is used where the function of the inner lining is different from that of the outer lining. It is co-extruded with PVC where the Hytrel is extruded first, which is followed by the PVC being extruded over it. It is designed to endure harsh and stressful conditions.
What are the Different Types of Rubber Tube?
The fabrication and production of rubber tubing are designed to develop types of rubber tubing for specialized conditions. Though there are a variety of materials used to make rubber tubing, the grade, and type of tubing are carefully selected for specialized applications, which leads to its different types.
Food Grade Rubber Tubing
The main concern of the food industry is tools that are safe and free of contaminants. Tubing used in the industry is required to follow very strict requirements to meet the standards of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which specifies the types of materials that are permitted to be used for food handling products. As with other industries, the food handling equipment has to be able to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions as well as the types of acids and chemicals used in food processing.
Medical Grade Rubber Tubing
Much like food-grade rubber tubing, there are strict guidelines for the production of medical-grade rubber tubing, which imposes severe design and construction requirements regarding the machining of the tubing and its ability to resist contaminants, degradation from use with chemicals, thermal damage, but have biocompatibility. The main purpose of the standards is for the protection of the patient.
The most common type of medical rubber tubing is silicone since it meets the standards established by the FDA per 21CFR177.2600. Medical rubber tubing is produced in various grades, levels of hardness, and sizes, depending on the application.
Conductive Rubber Tubing
Conductive rubber tubing is used to control the build-up of static in electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI) shielding. It is made from natural or silicone rubber and conducts electricity by the distribution of carbon or other particles in the raw material prior to fabrication.
Static electricity attracts dust that can cause sparks. Conductive rubber tubing reduces the friction that can ignite the dust. The tubing does not conduct electricity but moves or transports gases and liquids near electrically charged equipment.
Microbore Rubber Tubing
Microbore tubing is designed for use in the medical industry and comes in extremely small sizes. As with any products used for patient care, it has to meet FDA requirements for sterility and materials. It is used for intravenous lines and placement in veins and arteries with strong wall construction to allow for free flow of liquids such as blood or drugs and is ultra-smooth, inert, and sterile. Microbore tubing for medical use meets the USP Class VI biocompatible requirements for medical use.
Air Rubber Tubing
Air tubing moves pressurized air to actuators, valves, and tools. Extruding or mandrel methods can be used for the manufacture of air rubber tubing. It is constructed with an inner layer that is reinforced with fibers or a protective coating. When selecting air rubber tubing, the outside diameter (OD) determines the amount of pressure the tubing will be able to withstand. Small ODs tend to choke airflow.
Chemical Rubber Tubing
Chemical rubber tubing is designed for the movement of hydraulic fluids, acids, and toxic substances. It is co-extruded such that it has an inner and outer layer. The key characteristics of chemical tubing are its flexibility, resistance to absorption, and smoothness.
Heat Shrink Rubber Tubing
Heat shrink tubing is used to insulate, protect, and repair wires to extend their usefulness. Rubbers that are used for this process are abrasion, chemical, oil and acid resistant and able to withstand temperatures between -90° F to 390° F. Heat shrink rubber tubing has a dielectric strength of 500 to 800 V/mil, which is the strength tubing can handle before it begins to breakdown. The higher the dielectric strength, the better the tubing is at preventing heat, electricity, or signal from dispersing.
Fabric Reinforced
Fabric, cloth, or textile reinforced tubing has three parts, which are the reinforcing material, tube, and cover. The tube is made from synthetic rubber that is resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and oils, usually NBR. The reinforcing material is made from multiple layers of synthetic material that give the tubing a very solid and firm structure. The fabric and reinforced tubing are covered with a second layer of synthetic rubber that has the same properties as the first layer. The construction, structure, and arrangement of the materials produce highly durable and resilient tubing.
Where is Rubber Tubing used?
The flexibility and adaptability of rubber tubing have made it essential for use as a component in several industries. Rubber tubing is highly resilient and dependable as well as long-lasting. These qualities make it ideal for use in homes for transfer of water and chemicals and in the industry for applications involving hydraulic fluids and chemical processing.
Industries that Use Rubber Tubing
Automotive
Rubber tubing in the auto industry is referred to as hose and tubing. It is used as fuel lines, radiator hoses, for supplying lubricants, and part of cooling systems. The smooth operation of automobiles depends on rubber tubing being in excellent condition. Since rubber tubing has a long life span and history of dependability, it is the most widely used method for the movement of fluids in automobiles.
Agriculture
There are several varieties of rubber tubing used in agriculture. It is used to transfer grain, collect debris, and provide ventilation. Each application requires specially designed tubing. Flexible tubing is used to move abrasive materials such as animal feed, grain, and manure. A major use for agricultural tubing is for ventilation to ensure proper airflow for livestock. Agriculture rubber tubing is required to be chemical resistant due to the wide variety of chemicals used for food production and feeding.
Aerospace
The special conditions of air transport require rubber tubing that can withstand harsh weather conditions, radical pressure changes, and wide temperature variances. Flexible tubing or hose is used in aircraft for fluid systems to connect moving parts with stationary ones in locations that are subject to vibrations. Additionally, rubber tubing is used as a connector between metal tubing.
To meet the required strength, durability, and reliability for aerospace, synthetic rubbers are used to manufacture aircraft rubber tubing, which includes neoprene, butyl, and EPDM. The psi for aircraft tubing varies between 250 psi to 3000 psi.
Food Processing
Rubber tubing for food processing is extremely critical and has to be manufactured to meet the rigorous standards set by the FDA. One of the necessary properties of food-grade rubber tubing is the avoidance of kinking and the accumulation of contaminants or sediments to ensure easy flow and flushing. The walls of food-grade rubber tubing are thick to prevent kinking, but the tubing is lightweight and flexible. Since food products produce acids and chemicals, food-grade rubber tubing is resistant to those materials as well as alcohol and alkali. It is produced using a purity process to avoid the transfer of tastes and odors. Food grade rubber tubing is used with water, air, beverages, and dairy products.
Marine
There is a wide variety of tubing and hoses that are used for marine applications, which can be seen in the diagram below. Water hoses are used to pump engine cooling water, flush toilets, and cool air conditioning. Drainage hoses are found in the cockpit, sink, or shower and are resistant to kinks and abrasions. Drinking water hoses are made to FDA specifications to avoid bad-tasting water. Other hoses include bilge pumps and sanitation hoses, which have to be rugged for constant use.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Medical and pharmaceutical grade rubber tubing is normally produced using some form of synthetic rubber with silicone being the most common, which has very few compounding agents. The quality of medical and pharmaceutical grade rubber tubes includes having been tested as implantations in animals and humans, manufacturing conditions in adherence to FDA regulations, and exceptional quality control.
Medical grade rubber tubing is used to make feeding tubes, catheters, implants for long and short-term use, and syringe pistons. The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH), under FDA oversight, regulates medical and pharmaceutical grade rubber tubing.
The required properties for medical and pharmaceutical grade rubber tubing are odorless, non-toxic, inert, temperature stable, and superior chemical resistance. A key to meeting FDA regulations is the choice of materials used in the manufacturing process and the vulcanization or curing method.
Other Industries Using Rubber Tubing
- Chemical
- Construction
- Coolant
- Cryogenic
- Discharge
- Exhaust
- Fire
- Fresh air
- Garden or landscaping
- Heavy industry
- HVAC
- Oil or fuel
Any industry that requires the transmission, movement, or transport of liquids or gases depends on rubber tubing as an integral part of its operation.
How to store the rubber tubes?
Storage
Where rubber tubing is stored can have a significant impact on its usefulness. Some of the factors that influence or damage rubber tubing in storage include temperature, ozone or UV conditions, and abrasions.
Temperature: There are two types of temperature that influence rubber tubing, which is the temperature of liquids passing through the tubing and the outdoor and indoor temperatures. If the temperature is too hot or cold, the tubing will lose its usefulness.
Ozone and UV: Sun and ozone levels can do significant damage to rubber tubings such as creating cracks or dry rot. Rubber tubing for outdoor use should be thoroughly tested before being put into use.
Abrasion: If the rubber tubing is handled frequently or dragged over rough surfaces, it can suffer erosion or mechanical wear. This can be prevented by using rubber tubing made of more durable materials.
Chemicals
Only rubber tubing that is designed for chemical contact can withstand chemical exposure. Rubber tubing that can potentially come in contact with toxic substances should be rated to handle such exposure.
Special Functions
Rubber tubing comes in a wide array of sizes, configurations, grades, and purposes. The type of tubing should be selected to fit its application with the correct durability and characteristics.
ISO Regulations
ISO standards are guidelines for hoses and hose assemblies. The regulations cover:
- Sizes regarding minimum and maximum diameters
- Testing
- Reinforcing materials
- Hoses for specific purposes such as suction and gas transport
- Volumetric expansion
- Hydraulic usage
- Vacuum usage
- Abrasive lining
- Flammability
- Adhesion
- Storage and maintenance
- Measurement of flexibility and stiffness
- Types of fittings
Conclusion
- Rubber tubing, also known as rubber hose and rubber piping, is made of natural and synthetic rubber and is used to circulate and transport liquids and gases for household and industrial uses.
- Rubber tubing can be produced in a wide variety of tube diameters and wall thicknesses.
- The flexibility and adaptability of rubber tubing have made it essential for use as a component in several industries.
- Rubber tubing is distinctively different from another tubing because of its rubber content, which is an elastomer that has high strength and durability as well as being able to be stretched and deformed without being permanently damaged.
- The wide use of rubber tubing has led to the development of several different types of rubber to fit unique and specialized applications.









 sunhose
sunhose